
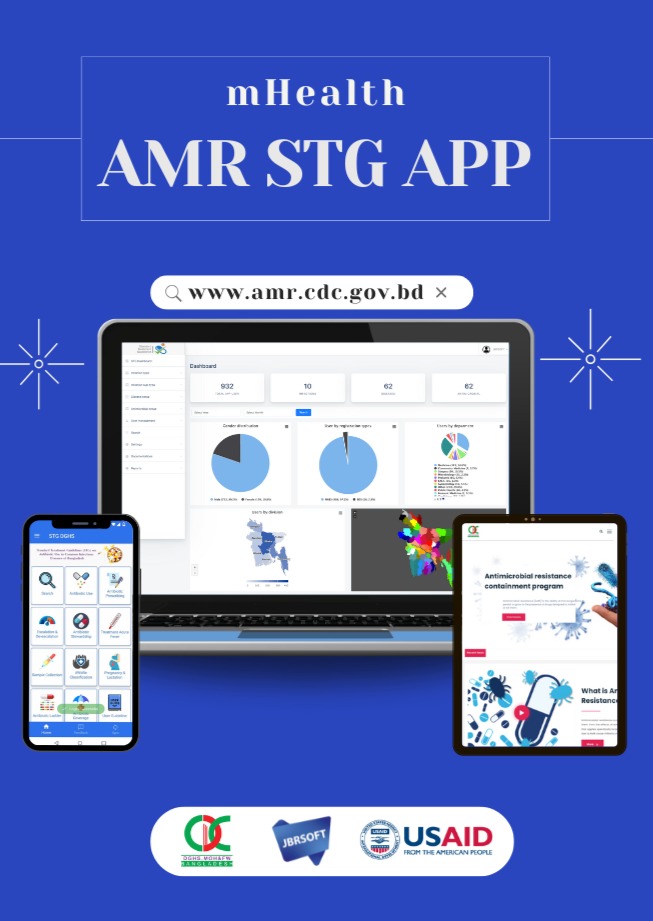
The AMR mHealth application offers a range of features and functionalities designed to enhance the management of AMR in common infectious diseases. By leveraging real-time data collection and analysis, clinicians can access crucial information on the prevalence of infectious diseases, the burden they impose on the population, and the most appropriate antibiotic treatments based on their susceptibility to AMR.
Antibiotic Resistance is a growing global public health threat that is imposing serious effects on management of the infectious diseases. The World Health Organization (WHO) and other international bodies identified antibiotic resistance as the biggest emerging threat for the globe, another pandemic. A National Strategy for Antimicrobial Resistance Containment (ARC) in Bangladesh was developed and approved by the National Steering Committee (NSC) and the National Technical Committee (NTC) with further recommendation of developing a National Action Plan (NAP). The causative microbes of common infectious diseases of Bangladesh are resistant to antibiotics, which include acute respiratory infection (ARI), gastrointestinal infection, tuberculosis (TB), urinary tract infections (UTI), neonatal infections (sepsis), ear infections (otitis media), typhoid fever, and skin & soft tissue infections (SSTIs). Due to lack of standard culture facility, diagnosis and treatment of common infections are mostly empirical. Consequently, the information that we need to design evidence-based intervention to contain antibiotic resistance is currently unavailable in Bangladesh. On this backdrop, Bangladesh has planned to develop a national standard treatment guideline for use of antibiotic.