



The Communicable Disease Control (CDC) program under the Directorate General of Health Services (DGHS) in Bangladesh is dedicated to safeguarding public health through the prevention, surveillance, and management of communicable diseases. Operating under the Ministry of Health and Family Welfare, the CDC employs a comprehensive approach encompassing antimicrobial resistance (AMR) containment, infection prevention and control (IPC), antimicrobial stewardship (AMS), and the One Health framework.
Antimicrobial Resistance (AMR) Containment: The CDC coordinates national efforts to combat AMR, recognizing it as a multifaceted challenge. By implementing the One Health approach, the program ensures collaboration across human, animal, and environmental health sectors to address AMR effectively.
Infection Prevention and Control (IPC): To enhance IPC practices, the CDC has developed national guidelines and conducted training programs for healthcare professionals. For instance, in collaboration with the World Health Organization (WHO), the CDC trained 65 physicians and nurses from various hospitals to strengthen IPC measures.
Antimicrobial Stewardship (AMS): The CDC promotes rational antibiotic use through the development of Standard Treatment Guidelines (STG) and the implementation of stewardship programs aimed at optimizing antimicrobial prescribing practices.
One Health Approach: Recognizing the interconnectedness of human, animal, and environmental health, the CDC adopts the One Health approach to address zoonotic diseases and other health threats comprehensively.
National Malaria Elimination and Aedes Transmitted Disease Control Program
Programs for Lymphatic Filariasis (LF), Soil Transmitted Helminthiasis (STH), and Little Doctors (LD)
Dedicated to eliminating visceral leishmaniasis, commonly known as kala-azar, through surveillance and treatment initiatives.
Addresses diseases transmitted from animals to humans, including rabies, Nipah virus, leptospirosis, and brucellosis. The program has developed national guidelines for managing animal bites to prevent rabies transmission
Antimicrobial Resistance Containment (ARC), Viral Hepatitis (VH), and Diarrhoeal Diseases Control Program
Programs for International Health Regulations (IHR), Migration Health, and Emerging and Re-emerging Diseases
Investigates and addresses the health impacts of climate change, including the emergence of climate-sensitive diseases.

The AMR mHealth application offers a range of features and functionalities designed to enhance the management of AMR in common infectious diseases. By leveraging real-time data collection and analysis, clinicians can access crucial information on the prevalence of infectious diseases, the burden they impose on the population, and the most appropriate antibiotic treatments based on their susceptibility to AMR.
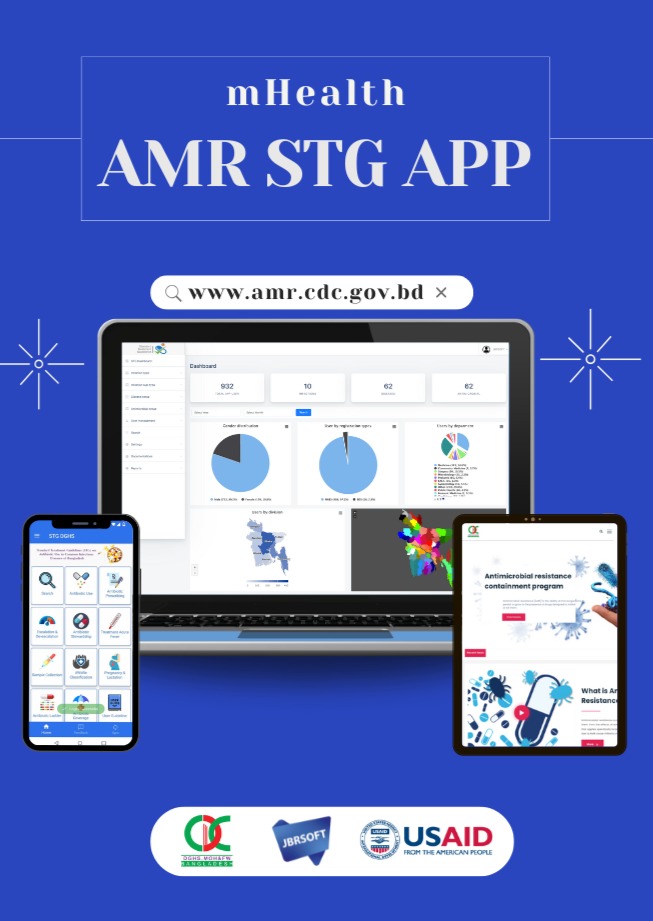
Antibiotic Resistance is a growing global public health threat that is imposing serious effects on management of the infectious diseases. The World Health Organization (WHO) and other international bodies identified antibiotic resistance as the biggest emerging threat for the globe, another pandemic. A National Strategy for Antimicrobial Resistance Containment (ARC) in Bangladesh was developed and approved by the National Steering Committee (NSC) and the National Technical Committee (NTC) with further recommendation of developing a National Action Plan (NAP). The causative microbes of common infectious diseases of Bangladesh are resistant to antibiotics, which include acute respiratory infection (ARI), gastrointestinal infection, tuberculosis (TB), urinary tract infections (UTI), neonatal infections (sepsis), ear infections (otitis media), typhoid fever, and skin & soft tissue infections (SSTIs). Due to lack of standard culture facility, diagnosis and treatment of common infections are mostly empirical. Consequently, the information that we need to design evidence-based intervention to contain antibiotic resistance is currently unavailable in Bangladesh. On this backdrop, Bangladesh has planned to develop a national standard treatment guideline for use of antibiotic.


incididunt ut labore et dolore magna aliqua. Quis ipsum suspendisse ultrices gravida. Risus commodo viverra .